Use of Honey in Wound Care – Effectiveness of Honey Wound Dressing
Table of Contents:
Introduction
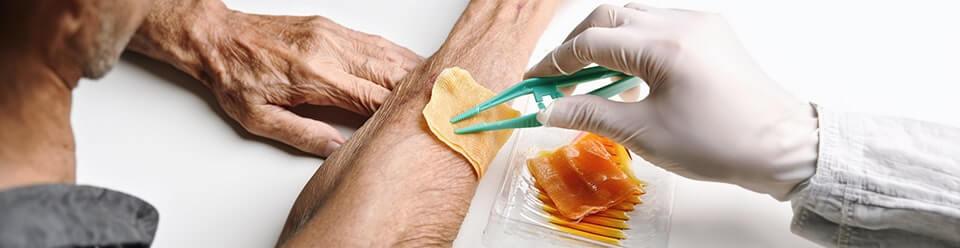
Honey has been cherished for centuries, not only as a delectable treat but also as a powerful wound treatment. In modern wound care, the application of honey in wound dressings has become standard practice. But what sets honey apart, and how does it surpass conventional dressings in promoting healing? Delve into the intricate world of medical-grade honey and explore the evidence supporting its effectiveness in wound healing.
What is Honey?
Medical-Grade Honey for Healing
Harnessing Honey's Healing Potential
The topical application of medical-grade honey positively impacts the wound healing process through multiple mechanisms. Its natural acidity, with a pH of around 3.5-4.5, aids in topical acidification of wounds, enhancing oxygen release from hemoglobin and promoting healing. Moreover, honey exhibits antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties, rendering it a highly effective wound treatment.
The antibacterial power of honey combats various microorganisms, including notorious bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus, thus expediting wound healing. Bacteria within wounds metabolize amino acids, leading to malodor. Honey wound dressings mitigate this issue by providing glucose as a preferential food source for bacteria, which avoids the production of odorous amines and sulfurs.
Unraveling the Enigma of Manuka Honey:
Forms and Applications of Honey Wound Dressings
Considerations and Future Research
While honey provides an alternative to harsh antiseptics and silver-containing products, patients with bee allergies must avoid honey-based dressings. Additionally, the selection of honey forms suitable for specific wound types may prove challenging.
Further research is essential to establish robust evidence regarding honey’s efficacy in wound healing. More randomized controlled trials are needed to compare different honey types and identify the active ingredients responsible for promoting wound healing.